-
About us
- About KR CEO KR History KR's Services Mission & Vision CI Organization
- Careers The Right People Job Location Recruitment
- Business Sustainability ESG Management Anti-Bribery Management Quality Management Health/Safety/Environment
- PR Center Digital News Room Publications PR Video Events Webzine
- Notice Board
-
Our Services
- Classification During Construction Introduction About KR EDAS KR EDAS Log in After Construction Introduction Transfer of Class and Certification KR Remote Survey Introduction Types of Remote Survey Survey application FAQ Existing Ships Condition Assessment Program PSC PSC Introduction PSC Information PSC Deficiency Data PSC Check List PSC Regional MOUs PSC Annual Report PSC Link Detention Notice USCG/PARIS MoU Information LNG LNG Carrier LNG Fueled Ship LNG Bunkering Ship Oil Major Inspection Overview OCIMF Annual Report Technical Information Link
- ISM/ISPS/MLC ISM ISPS MLC
- Statutory Services Statutory Survey Foreign Governments Status of Authorization KR at IMO
- Approval of Class Equipment General Scope Approval of Manufacturing Process Type Approval Design Approval Procedure Flow Chart of Marine & Ocean Equipment Approval Flow Chart of Design Approval Documents e-MESIS Approval Lists EU RO-MR Introduction Application Form Documents to be Submitted Approval List
- Cyber Security Certification Service Certification Service Ship & Company Certification Cyber Security Type Approval Software Conformity Certification Technical Service Awareness Training Newsletter International Response
- Certification System Certification Third Party Inspection Global Certification AIP(Approval In-Principle) Introduction Procedure Track Record Renewable Energy Lender’s Technical Advisor for renewable energy Wind Energy
- Naval Service NSAP Rules and standards for naval vessels Core technology and technical support
- Oil & Gas Asset Integrity Sustainability and Management System(AISMS) Introduction Integrated Integrity Management System (IIMS) Integrity Diagnostic and Data Management Corrosion Management Plan and Framework Quality Assurance, Control and Surveillance Digitalization and Paperless Inspection Scheme Global Third Party Inspection Network
- Service Supplier SeaTrust - TM Service Supplier Download Service Supplier Search
- Customer Services Register of Ships EU Ship-info Useful Links
- Online Application Introduction Application Form On-line Application Service On-line application for ISM/ISPS & MLC Application Status
-
Decarbonization & Digitalization
- Decarbonization KR Decarbonization Portal KR Decarbonization Magazine
- Digitalization Smart & Autonomous Ship AI Driven Inspection Condition Based Inspection Digital Twin
- Digital Solutions KR-DAON KR e-Fleet e-Cert Introduction Flag Acceptance User Guide FAQ KR e-Fleet EACSD e-Cert Verification e-MESIS KR-CON Fit-For-Purpose Key Functions Order Online KR-NBM KR-EDAS KR-PILOT KR-POWER EACSD KR GEARs SeaTrust Software KR-ERS About KR-ERS Flow Chart for KR-ERS Service Registration KR-SteelCoil About KR-SteelCoil KR-SteelCoil Program
-
Rules & Solutions
- Classification Technical Rules Classification Technical Rules Service Establishment and amendment history of Classification Technical Rules Circulars Guidelines External opinion inquiry on the amendment Part 1, Forms (Survey Programme etc)
- Information & Updates Briefings of IMO SOLAS/MARPOL/Others Port Rule Information ISM/ISPS/MLC SOPEP/SMPEP Rules and Technical Information
- Hull Technology Research Seakeeping Hydrodynamics R&D related to CCS Arctic Technology KR Rules & Guidance on Hull Structures Application Technologies
- Engineering Offshore Platform Commercial Ship Naval Ship
- System Risk Assessment R&D Activities on Risk Assessment Risk Assessment
-
About us
- About KR CEO KR History KR's Services Mission & Vision CI Organization
- Careers The Right People Job Location Recruitment
- Business Sustainability ESG Management Anti-Bribery Management Quality Management Health/Safety/Environment
- PR Center Digital News Room Publications PR Video Events Webzine
- Terms of Website Use
- Notice Board
- Survey
-
Our Services
- Classification During Construction Introduction About KR EDAS KR EDAS Log in After Construction Introduction Transfer of Class and Certification KR Remote Survey Introduction Types of Remote Survey Survey application FAQ Existing Ships Condition Assessment Program PSC PSC Introduction PSC Information PSC Deficiency Data PSC Check List PSC Regional MOUs PSC Annual Report PSC Link Detention Notice USCG/PARIS MoU Information LNG LNG Carrier LNG Fueled Ship LNG Bunkering Ship Oil Major Inspection Overview OCIMF Annual Report Technical Information Link
- ISM/ISPS/MLC ISM ISPS MLC
- Statutory Services Statutory Survey Foreign Governments Status of Authorization KR at IMO
- Approval of Class Equipment General Scope Approval of Manufacturing Process Type Approval Design Approval Procedure Flow Chart of Marine & Ocean Equipment Approval Flow Chart of Design Approval Documents e-MESIS Approval Lists EU RO-MR Introduction Application Form Documents to be Submitted Approval List
- Cyber Security Certification Service Certification Service Ship & Company Certification Cyber Security Type Approval Software Conformity Certification Technical Service Awareness Training Newsletter International Response
- Certification System Certification Third Party Inspection Global Certification AIP(Approval In-Principle) Introduction Procedure Track Record Renewable Energy Lender’s Technical Advisor for renewable energy Wind Energy
- Naval Service NSAP Rules and standards for naval vessels Core technology and technical support
- Oil & Gas Asset Integrity Sustainability and Management System(AISMS) Introduction Integrated Integrity Management System (IIMS) Integrity Diagnostic and Data Management Corrosion Management Plan and Framework Quality Assurance, Control and Surveillance Digitalization and Paperless Inspection Scheme Global Third Party Inspection Network
- Service Supplier SeaTrust - TM Service Supplier Download Service Supplier Search
- Customer Services Register of Ships EU Ship-info Useful Links
- Online Application Introduction Application Form On-line Application Service On-line application for ISM/ISPS & MLC Application Status
-
Decarbonization & Digitalization
- Decarbonization KR Decarbonization Portal KR Decarbonization Magazine
- Digitalization Smart & Autonomous Ship AI Driven Inspection Condition Based Inspection Digital Twin
- Digital Solutions KR-DAON KR e-Fleet e-Cert Introduction Flag Acceptance User Guide FAQ KR e-Fleet EACSD e-Cert Verification e-MESIS KR-CON Fit-For-Purpose Key Functions Order Online KR-NBM KR-EDAS KR-PILOT KR-POWER EACSD KR GEARs SeaTrust Software KR-ERS About KR-ERS Flow Chart for KR-ERS Service Registration KR-SteelCoil About KR-SteelCoil KR-SteelCoil Program
-
Rules & Solutions
- Classification Technical Rules Classification Technical Rules Service Establishment and amendment history of Classification Technical Rules Circulars Guidelines External opinion inquiry on the amendment Part 1, Forms (Survey Programme etc)
- Information & Updates Briefings of IMO SOLAS/MARPOL/Others Port Rule Information ISM/ISPS/MLC SOPEP/SMPEP Rules and Technical Information
- Hull Technology Research Seakeeping Hydrodynamics R&D related to CCS Arctic Technology KR Rules & Guidance on Hull Structures Application Technologies
- Engineering Offshore Platform Commercial Ship Naval Ship
- System Risk Assessment R&D Activities on Risk Assessment Risk Assessment
Service
-
Item Prepared for ERS Registration
-
1. In case of ships assigned with KR ERS notation, the following data are inputted and stored into the database, so that a prompt activation of KR ERS program can be made possible in an emergency situation.
-
1. Hull Offset data (Hull form data) input [Ref. to Fig. 1~2]
- Hull form date input
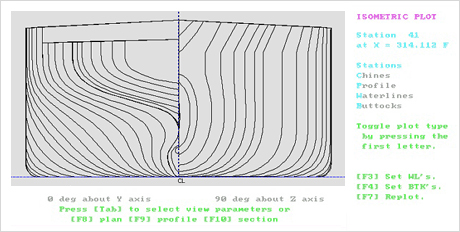 Fig.1) 301K VLCC Body Plan
Fig.1) 301K VLCC Body Plan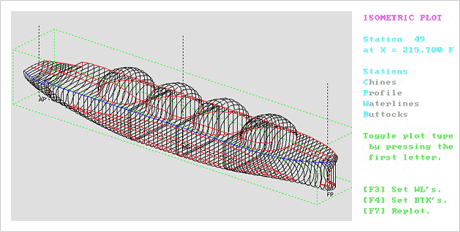 Fig.2) Moss Type LNG Carrier
Fig.2) Moss Type LNG Carrier -
2. Compartment Offset data input [Ref. to Fig. 3~7]
- watertight compartment form data input
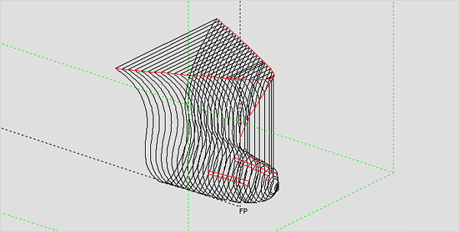 Fig.3) FPT of LNG Carrier
Fig.3) FPT of LNG Carrier Fig.4) No1. Cargo Tank of LNG Carrier
Fig.4) No1. Cargo Tank of LNG Carrier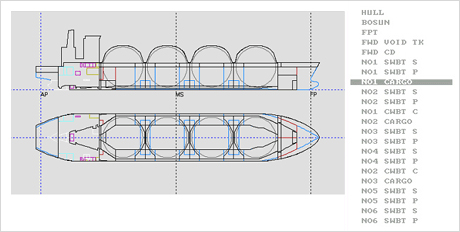 Fig.5) Defined Tanks Arrangement of LNG Carrier
Fig.5) Defined Tanks Arrangement of LNG Carrier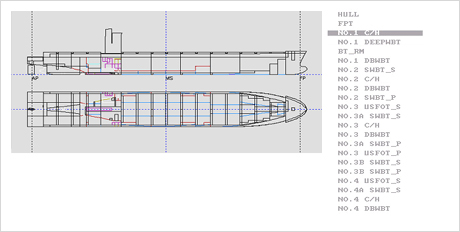 Fig.6) Tanks Arrangement of 5500TEU Container
Fig.6) Tanks Arrangement of 5500TEU Container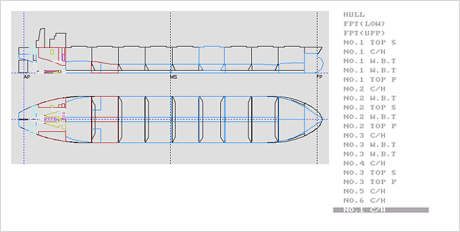 Fig.7) Tanks Arrangement of 161K Bulk Carrier
Fig.7) Tanks Arrangement of 161K Bulk Carrier -
3. Section Modulus Editor (Ref. to Fig. 8)
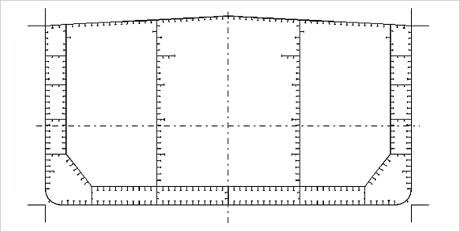 Fig.8) Midship Section of VLCC
Fig.8) Midship Section of VLCC -
4. Ship Data Input (Ref. to Fig. 9~10)
- Light Ship Data (Weight, Center) input
- Input a specific character of cargos and tanks
- Hydrostatic Table input manually/automatically
- Cross Curves input manually/automatically
- Bonjean Table input manually/automatically
- Required GM Curves input manually/automatically
- Light Weight Distribution data input
- Allowable Strength (S.F/B.M, SAG/HOG, SEA/HARBOR) data input
- Section Modulus Data input manually/automatically
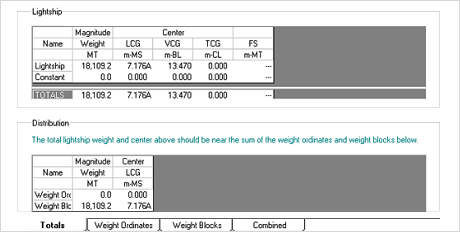 Fig.9) Light Ship Define Mode
Fig.9) Light Ship Define Mode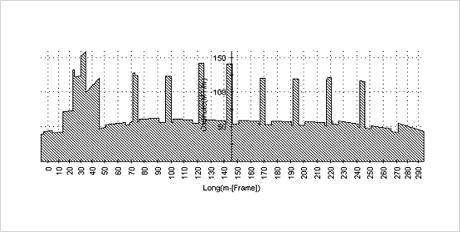 Fig.10) Light Weight Distribution
Fig.10) Light Weight Distribution
-
-
2. By using the basic data stored into the database, ERS team carries out following calculations through salvage program in advance.
- Hydrostatic and Bonjeandata Cross curves data Trim and stability summary in intact condition
-
3. In case of ships assigned with additional notation named ERS(D), worldwide weather forecasts are prepared to predict the vessel’s drift and oil spill transport for several days from anywhere the incident occurred.
-
1. MetOcean forecast data
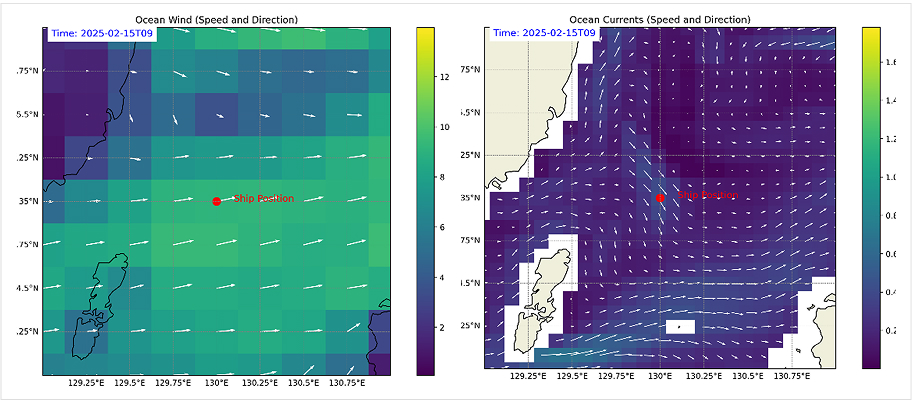 Fig. 11) Metocean forecast data(Current, Wind, etc.)
Fig. 11) Metocean forecast data(Current, Wind, etc.)- from the NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) or ECMWF (European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts)
-
-
-
Available Analysis by Using KR's Salvage Program
-
1. Intact Loading Condition(Ref. to Fig. 11∼14) Salvage program can check over the intact stability and longitudinal strength like the loading computer used onboard.
-
1. Cargo(Tank, Bulk, Container) loading condition input
-
2) Using the storage data in Ship Data Entry, following calculations is done.
- Trim & Stability
- GZ
- Longitudinal Strength (S.F , B.M)
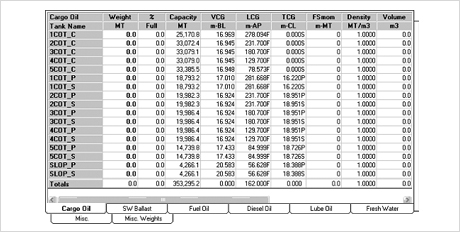 Fig.12) Tank & Cargo Weights Entry Mode
Fig.12) Tank & Cargo Weights Entry Mode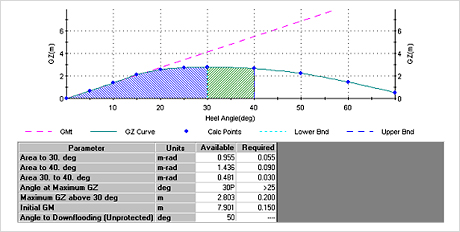 Fig.13) Trim & Stability Summary
Fig.13) Trim & Stability Summary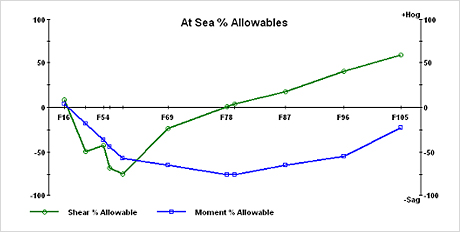 Fig.12) Tank & Cargo Weights Entry Mode
Fig.12) Tank & Cargo Weights Entry Mode Fig.13) Trim & Stability Summary
Fig.13) Trim & Stability Summary
-
-
2. Salvage Response (Ref. to Fig. 15~19)
- This is the main function of Salvage Program. Salvage Program calculate residual stability, buoyance, longitudinal strength and oil outflow etc, in case of casualties - flooding, stranding and structural damage - , and establish the most effective salvage countermeasure.
-
1 Using the intact loading data before the accident
-
2. Input a damaged condition such as damaged compartment and structural damage include their
- location : Salvage program simulate the real accident situation in way of the damaged data (Flooding, stranding, etc) input. Structural damages are also made in the corresponding transverse section.
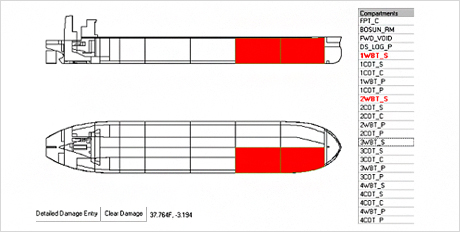 Fig.14) Specify Damage Compartments
Fig.14) Specify Damage Compartments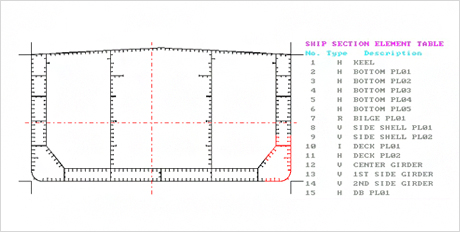 Fig.15) Specify Structural damage
Fig.15) Specify Structural damage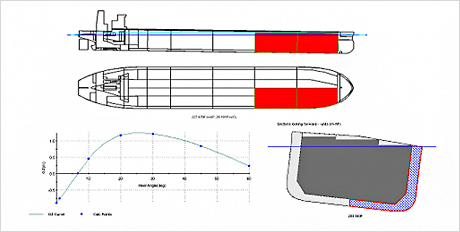 Fig.16) Free floating after damage
Fig.16) Free floating after damage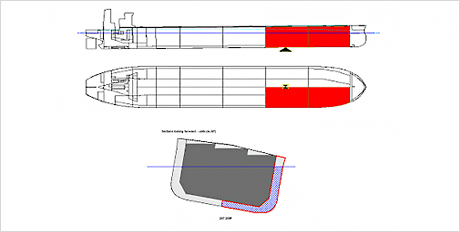 Fig.17) Damage and strand
Fig.17) Damage and strand -
3. Wave and Wind Condition Input
-
Wave
- - Salvage Program can calculate the wave height, wavelength and wave position(hogging, sagging)
- - consider the wave condition at the place that accident happen. If the sea condition is the real extreme case, the program consider the real wave height, 90~100%L wavelength and sagging condition.
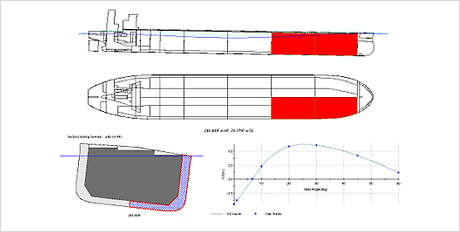 Fig.18) Considering Wave
Fig.18) Considering Wave-
Wave
- - Salvage program can consider the effect of wind applied to the side projected plane of the ship. The program need to input a wind speed, coefficient of resistance, wind pressure, area and arm etc.
-
Wave
-
4. Following Condition is able to calculate
- Free Floating
- One Pinacle
- Two Pinacle
- Shelf Stranding
- Stranding after tidal change
-
5. Calculation Summary
- Stability after Damage
- Strength after Damage : It can consider displacement and bucking align the longitudinal hull direction.
- Outflow/Flooding in Compartment
- Oil Outflow
-
6. It is possible to compare and examine the salvage procedure
-
3. The ship with ERS(D) notation can be provided the trajectory predictions of Vessel draft & oil spill transport for several days following an incident. These trajectory predictions support risk assessment and the development of mitigation plans by considering environmental factors such as ocean currents, wind, and temperature, thereby enable effective and timely response planning.
-
1. Vessel Drift
- This service predicts vessel drift using the OpenDrift (https://opendrift.github.io/), developed by the Norwegian Meteorological Institute.
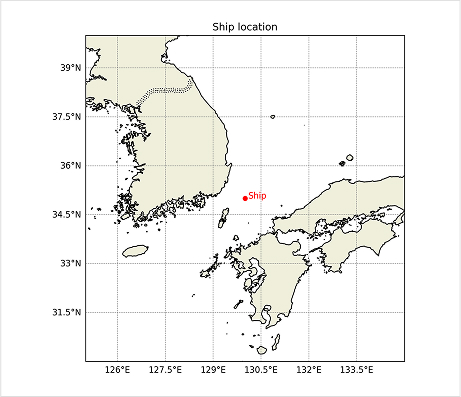 Fig. 19) Ship location
Fig. 19) Ship location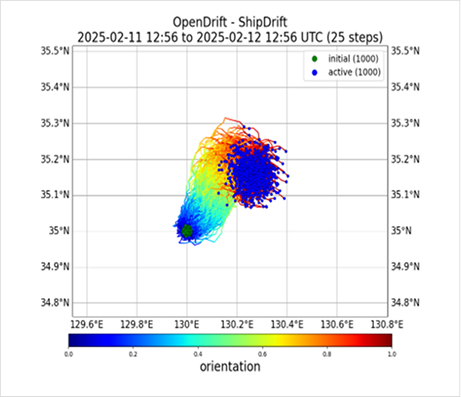 Fig. 20) Ship trajectory
Fig. 20) Ship trajectory -
2. Oil Spill Trajectory
- This service provides visualized oil spill trajectory predictions using OpenDrift (https://opendrift.github.io/), developed by the Norwegian Meteorological Institute.
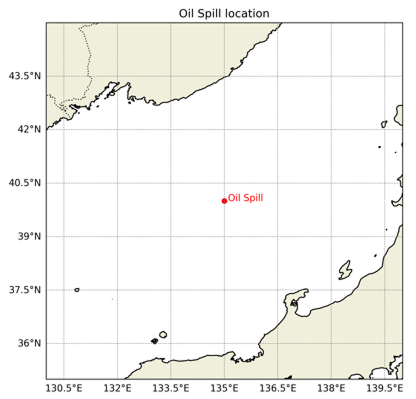 Fig. 22) Ship location
Fig. 22) Ship location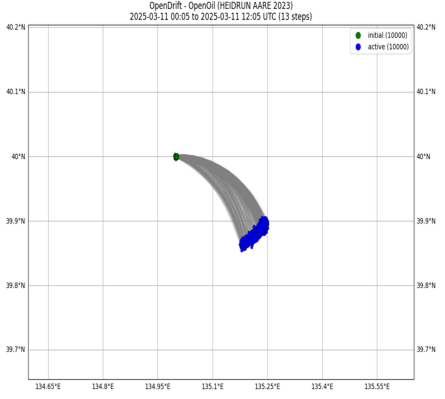 Fig. 23) Oil trajectory
Fig. 23) Oil trajectory
-
-
Technical Review of Salvage Plan
-
To adjust the excessive trim or heeling cause of flooding or stranding and to guarantee a sufficient stability, or to refloat the stranded ship, follwoing actions should be taken.
- Ballasting or de-ballasting
- Weight(Oil) Transfer: The weight(oil) or ingress water(ballast water) shall be transferred to other place in the ship by using the available piping system or crane, etc.
- Lightering: The weight(oil) or ingress water(ballast water) shall be transferred outboard by using the available piping system or crane, etc.
- Maintaining the constant air-pressure in damaged compartment: In case of bottom damage, the pressurized air should be flowed into flooded compartment to reserve the compartment buoyance. It can be possible to use the equipment.
- Tidal Change: If the ship is stranded, tidal change is very important. Considering this point help to find the minimum(optimum) way to refloat.
· Inquiry
- Dept. Stability & Tonnage Team
- TEL +82 70 8799 8488
- FAX +82 70 8799 8419
- E-mail krers@krs.co.kr



