-
- KR Celebrates 63 Years with Special Technical Seminar
- Paper proposing effective implementation of CII published in international journal Ocean Engineering
- KR Grants Approval in Principle to SHI's LCO2 Carrier
- KR Approves Jointly Developed Methanol-Fueled MR Tanker
- KR Grants First New Technical Qualification (NTQ) Statement for HiNAS-Control
- KR Awards Approval in Principle to HD Hyundai Heavy Industries' Innovative Tank Shape (Hi-ICON) with Sloshing-Restrained Technology
- KR Celebrates 63 Years with Special Technical Seminar
- Paper proposing effective implementation of CII published in international journal Ocean Engineering
- KR Grants Approval in Principle to SHI's LCO2 Carrier
- KR Approves Jointly Developed Methanol-Fueled MR Tanker
- KR Grants First New Technical Qualification (NTQ) Statement for HiNAS-Control
- KR Awards Approval in Principle to HD Hyundai Heavy Industries' Innovative Tank Shape (Hi-ICON) with Sloshing-Restrained Technology
-
- KR Celebrates 63 Years with Special Technical Seminar
- Paper proposing effective implementation of CII published in international journal Ocean Engineering
- KR Grants Approval in Principle to SHI's LCO2 Carrier
- KR Approves Jointly Developed Methanol-Fueled MR Tanker
- KR Grants First New Technical Qualification (NTQ) Statement for HiNAS-Control
- KR Awards Approval in Principle to HD Hyundai Heavy Industries' Innovative Tank Shape (Hi-ICON) with Sloshing-Restrained Technology
Writers
Islam MD Shafiqul and Kim Beom-il
Ship & Offshore Technology Team
1. Overview
With global warming intensifying and consequent climate change a worldwide issues, countries and major companies around the world are promoting policies for Net Zero, as well as developing industrial ecosystems and other related projects as a response. The shipbuilding and maritime industry have been developing technologies for transporting eco-friendly energy, and the use of low-flash point fuels is recognized as an effective method of complying with the requirements of exhaust gas emission regulations.
Currently, technology development for LNG-fueled ships has been progressed, and as the number of ships in actual operation increased, it is important to analyze and evaluate ship operational risk scenarios.
An example is the use of pressurized gas. Should an accident occur in the process system or related equipment maintenance is required, , pressurized gas is released through a vent mast or other vent to drop the pressure in the system. However this causes the malfunction of equipment around the vent or causes accidents such as fire or explosion by ignition sources. Most dangerous is the risk that the operator inhales the released gas which could cause injury, suffocation or death..
The flammable (explosive) area can be defined by estimating the shape and size of the flammable gas cloud which develops once liquefied natural gas disperses from the vent. This LNG dispersion analysis allows the vessel or system to be designed taking these results into consideration. KR has now published (January 2023) guidelines for liquefied natural gas dispersion analysis.
2. Main Contents
The LNG dispersion analysis to be performed using the guidelines provides an estimation of the shape and size of the flammable gas cloud developed by the dispersion of liquefied natural gas from the vent mast or other vent outlet in normal or abnormal scenarios during system operation.
○ Chapter 1 Introduction
• Section 1 Genera
- Definition, objectives and execution time of LNG dispersion analysis.
• Section 2 Terms and Definitions
• Section 3 Model and Software for LNG Dispersion Analysis
- A brief explanation for the three analysis models (Workbook, Integral and CFD) that can support the LNG dispersion analysis is included, and representative software for each analysis model can be identified.
○ Chapter 2 LNG Dispersion Analysis Conduct
• Section 1 Procedure for LNG Dispersion Analysis
- The procedure (Preparation, Conduct and Follow-up work) for LNG dispersion analysis is introduced in this section.
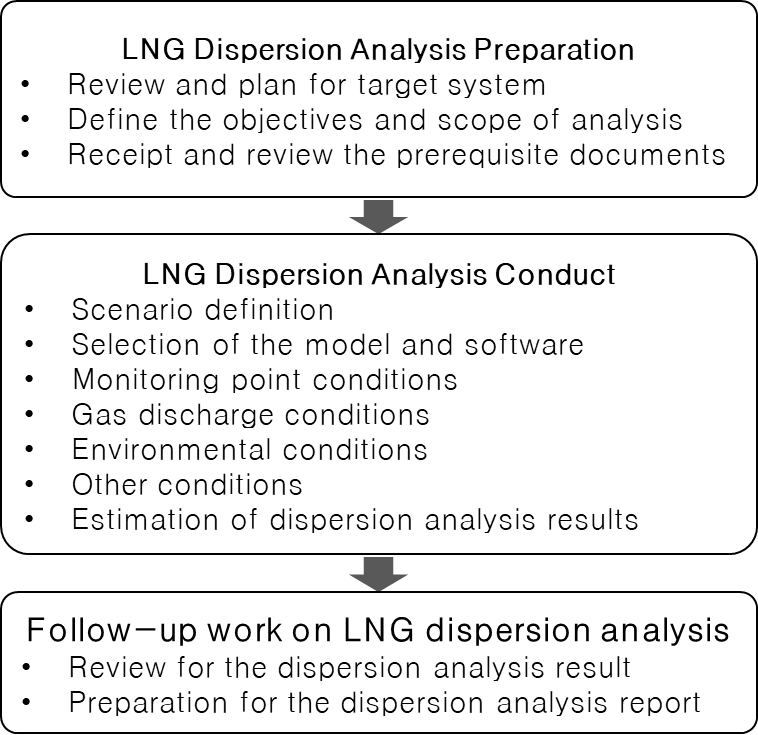
Figure 1. Procedure for LNG dispersion analysis (Source: KR)
• Section 2 LNG Dispersion Analysis Preparation
- The contents of the target system review and planning are included and the objectives and scope of analysis to be obtained through dispersion analysis are explained in this section. In addition, the necessary information for conducting LNG dispersion analysis is suggested, including information related to design, arrangement and operation concept as well as environmental conditions of the sea or field where the target system would be operated.
• Section 3 LNG Dispersion Analysis Conduct
- LNG dispersion analysis mentioned in the guidelines is not a verification task for an accident that has already occurred, but an analysis task to prevent accidents and minimize damage in preparation for a potential accident scenario. Therefore, it is necessary to prepare the analysis by pre-supposing a scenario in which an accident with a high probability or the worst accident that could occur among several potential accident scenarios. For this reason, a high degree of understanding of the scenario, selection of the model & software, and the conditions of monitoring point (concentration of interest, averaging time, etc.), gas discharge (discharge flowrate, pressure, composition, etc.) and environment (wind direction, speed, atmospheric stability, etc.) for the dispersion analysis is required, and explanations for these conditions are included in the guidelines.
○ Chapter 3 LNG Dispersion Analysis Report
• Section 1 General
- The general information for the report such as objectives, main contents and procedures.
• Section 2 Contents
- The essential contents to be included in the report, such as the explanation of the target system, and the configuration of report is suggested as an example.
○ Annex 1 Safety Zone Establishment for LNG Transfer and Bunkering Operations
- The development of a flammable gas cloud and then accidents such as explosion and fire may arise in various circumstances, such as ship to ship, truck to ship and port to ship, if a leak occurs during the LNG transfer or bunkering operations. To control these risks, the areas that can be affected by the flammable gas cloud from leakage must be designated in advance to ensure safety. Measures that can be taken such as active monitoring activities and restrictions on surrounding movements must be carried out to reduce the foreseeable risks. Annex 1 suggests a brief description of safety zone and methods (deterministic and probabilistic) for zone establishment to carry out the LNG transfer and bunkering operations safely.
3. Conclusion
Users can identify risk scenario for dispersion analysis and improve the understanding for conditions of monitoring, gas discharge, environment, etc., through these guidelines. In particular, the shape and size of flammable gas cloud developed by LNG or natural gas released from vent mast or other vent outlet can be estimated as analysis results. The flammable (explosive) area can be defined, and the arrangement of accommodation, door, HVAC intake, etc., can be reviewed with overall safety aspects based on analysis results. Furthermore, hazardous accidents caused by the dispersion of liquefied natural gas can be prevented.
Appropriate analysis and zone establishment for the safety zone considering Annex 1 Safety Zone Establishment for LNG Transfer and Bunkering Operations can minimize the risk of leakage accident with operational safety management and protect the personnel and property through physical separation by zone establishment.
